Gtm Server-Side Vs Client-Side | GTM server-side tagging offers more control over data and privacy, while the client-side relies on the user’s browser. The server side runs on a server, handling requests sent by the website, and the client side executes in the browser, managing user interactions directly.
Understanding the difference between GTM (Google Tag Manager) server-side and client-side tagging is crucial in the world of web analytics and marketing. Server-side tagging provides a robust framework for handling sensitive data, reducing webpage load times, and enhancing security by processing data on a secured server.
This approach minimizes the amount of JavaScript executed in the user’s browser, thereby offering a cleaner and faster browsing experience. On the other hand, client-side tagging is the traditional method where tags are directly triggered in the user’s browser upon certain actions like pageviews or clicks. This method is simpler to implement and allows for real-time data collection and immediate feedback on user interactions. Each method comes with its distinct advantages, and choosing between them depends on the specific needs and resources of your website.
Client-side And Server-side Tagging Basics
Welcome to the world of digital analytics and tracking, where understanding the fundamentals of client-side and server-side tagging is essential for any digital marketer or web analyst. In this section, we delve into the basics, unravel the differences, and explore the roles of tags in web analytics to help you optimize your online presence effectively.
The Role Of Tags In Web Analytics
Tags are small pieces of code that track and collect data on your website. They help you understand user behavior and enhance user experience. Think of them as digital informants that report every click and scroll back to your analytics dashboard.
- Track page views and user interactions.
- Collect data for analytics and marketing platforms.
- Enable remarketing and audience building.
Differences Between Client-side And Server-side
Getting a clear grasp of client-side and server-side processes will transform your tagging strategy.
| Client-Side Tagging | Server-Side Tagging |
|---|---|
| Executes tags in the user’s browser. | Runs tags on a server, usually in the cloud. |
| Limits data privacy control. | Offers more data security and privacy options. |
| Can slow down page load times. | Improves website performance. |
| Depends on browser compatibility. | Not dependent on the user’s browser. |
Choosing between client-side and server-side tagging depends on your website’s needs, data privacy requirements, and resources.
Exploring Client-side Tagging
Client-side tagging plays a key role in modern web analytics. It involves collecting data directly from the user’s browser. Let’s dive into what client-side tagging is all about and scope out its pros and cons.
How Client-side Tagging Works
When a user visits a webpage, client-side tags fire up. These tags are small pieces of code embedded on the page. They send user interaction data to various tracking platforms.
- The user opens a web page
- Tags load with the page
- Interactions tracked in real-time
- Data sent to analytics servers
Advantages Of Client-side Tagging
Client-side tagging boasts several benefits.
- Easy Integration: Adding tags is usually simple, with many platforms providing user-friendly interfaces.
- Real-Time Data: Capture user actions the moment they happen.
- Rich Insights: Collects detailed information, enriching data analysis.
Limitations And Privacy Concerns
The method isn’t foolproof though.
| Limitation | Details |
|---|---|
| Browser Dependency | Reliant on the user’s browser functioning properly. |
| Performance Impact | May slow down page load times. |
| Privacy Issues | Risks with handling personal data. |
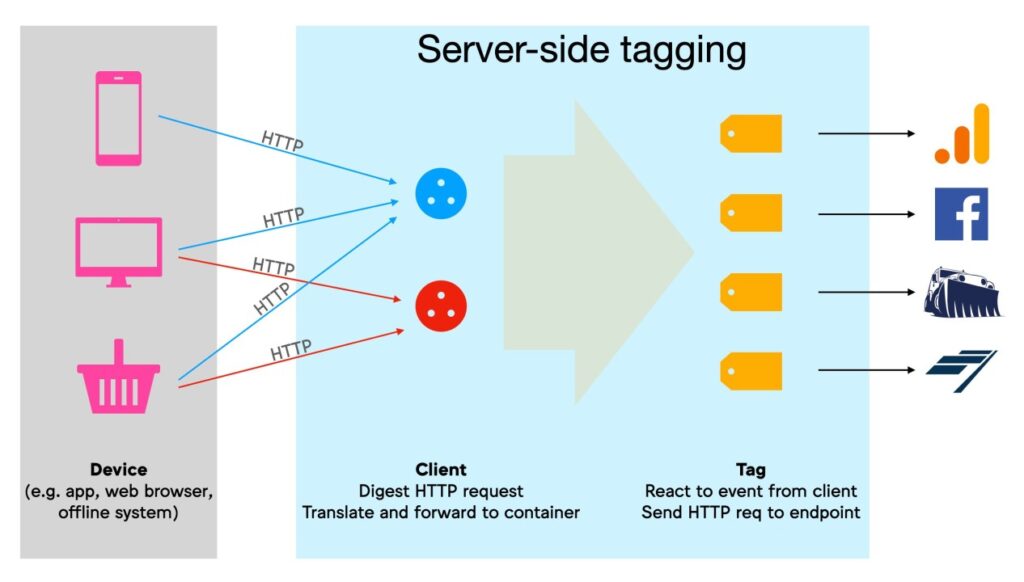
Diving Into Server-side Tagging
Server-side tagging shifts much of the data processing from the user’s browser to a server. This powerful move allows for enhanced performance, improved data security, and greater data control. Let’s uncover the layers of server-side tagging and see why it’s changing the game for websites and data processing.
Functionality Of Server-side Tagging
At its core, server-side tagging involves moving tags off the client side (like a user’s browser) and onto a server. This method allows for streamlined user experiences as it reduces browser load. Here’s what it involves:
- Collecting event data from the client.
- Sending data to a server.
- Processing and forwarding data from the server to analytics platforms.
By handling requests through a server, websites can load faster and provide smoother interactions for users.
Enhancing Data Security And Privacy
With server-side tagging, data privacy climbs to a new level. This approach provides:
- Tighter control over data collection.
- Reduced risk of sensitive data exposure.
- Compliance with strict privacy regulations.
Data sent directly to a server can be scrubbed and anonymized before reaching third parties, bolstering user privacy.
Potential Drawbacks
Though server-side tagging has numerous benefits, it is not without challenges:
| Drawback | Details |
|---|---|
| Complexity | Setup requires technical expertise and resources. |
| Server Costs | Running a server incurs additional costs. |
| Data Management Policies | Organizations must ensure compliance with data policies. |
Organizations must weigh the costs and complexity of server-side tagging against its benefits.

Credit: infotrust.com
Performance Impact Assessment
In the realm of web analytics, tag management is a vital factor for performance. ‘Performance Impact Assessment’ carefully weighs how GTM (Google Tag Manager) server-side versus client-side implementations influence websites. Let’s dissect the effects on site speed user experience, and resource efficiency.
Site Speed And User Experience
User engagement hinges on site speed – a fast website equals a happy visitor. A split-second delay can mean a lost customer. That’s where the GTM server-side steps in:
- Server-side tagging limits the client’s load, moving part of the work to a server. This results in snappier page loads.
- Browser work is reduced, so content pops up quickly for users. Better user experience becomes a reality.
On the other hand, client-side GTM carries the baggage of a heavier browser workload. It directly impacts user wait times:
- More scripts run on the user’s device, bogging down speed. Every millisecond counts.
- Securing user patience becomes harder with a sluggish interface.
Resource Efficiency And Optimization
Resource management is a top priority for websites aiming for peak performance. GTM’s server-side model is a game-changer here:
- Reduced resource strain on the client side ensures a leaner, optimized experience.
- Data processing shifts to the server side, which generally has more power.
Considering the client approach, individual devices bear the weight of processing:
- Each visitor’s device must work harder, affecting the speed and battery life.
- Optimizations are tougher to implement as variations in devices create inconsistent experiences.
So, while client-side GTM is easier to set up, server-side tagging is the efficient choice for high-traffic, performance-focused websites. It ensures smoother experiences and better resource management across the board.
Data Control And Ownership
Data control and ownership are critical in today’s data-driven world. With the rise of digital marketing, the way data is collected and managed has become a focal point. Two key approaches shape data management: server-side and client-side tagging. Each method offers unique control and ownership capabilities. Understanding these can empower businesses to make informed decisions on data privacy and efficiency.
Managing Data Flow With Server-side Tagging
Server-side tagging shifts the control of data from the user’s browser to your server. This allows for a more secure environment where sensitive data is better protected. Here are the key benefits:
- Enhanced Data Security: By processing data on the server, exposure to external threats is reduced.
- Improved Load Times: Fewer scripts in the user’s browser can lead to faster page loading.
- Customization: Tailored data processing and handling to fit precise business needs.
Adopting server-side tagging means owning the data flow process fully. It gives businesses more granular control over the data they collect and how it’s used.
Data Visibility In Client-side Tagging
Client-side tagging involves handling data where interactions occur — in the user’s browser. While it’s simpler to implement, data visibility plays a major role:
- Direct Interaction Tracking: Real-time data capture from the user’s actions on a webpage.
- Third-Party Script Dependency: Relies heavily on external scripts, such as Google Analytics.
- User Experience Transparency: Clear visibility on how their data is being used, which can improve trust.
With client-side tagging, conducting data tracking is transparent, but it also means data is more susceptible to being manipulated by browser settings like ad blockers.
Compliance With Data Regulations
Compliance with Data Regulations is a crucial aspect for businesses operating online. Companies must adhere to legal standards, like GDPR and CCPA, to safeguard user data. Understanding the differences between GTM server-side and client-side becomes vital in achieving this compliance.
GDPR and CCPA Implications
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) set strict rules for handling data. GTM server-side can help ensure that data is processed in secure environments, reducing the risk of breaches.
- Reduced data exposure: Server-side handling minimizes data sent to the client’s browser.
- Enhanced control: Tighter data processing control enables compliance with GDPR and CCPA.
Client-side GTM, however, sends data from the user’s browser to third parties. It may lead to increased risk if not managed properly.
- Data vulnerability: Sending data through the browser could expose sensitive information.
- Dependent on the user’s browser: Some users might block scripts, affecting data accuracy and compliance.
Choosing The Right Approach For Compliance
Selecting the correct GTM setup needs an understanding of your data processes. Proper implementation is key to abiding by laws.
- Assess data flow: Scrutinize how data moves through your systems.
- Prioritize security: Opt for server-side when dealing with highly sensitive data.
- Respect user consent: Client-side requires user permission for tracking, crucial for legal compliance.
Server-side offers more control and security for your data. Client-side is easier but may require additional steps to ensure compliance.
Choose wisely based on your specific data regimen. Keep user privacy at the forefront to maintain trust and legal compliance.
Scalability And Maintenance
Choosing the right Google Tag Manager environment is crucial for your online success. Whether you select server-side or client-side depends on various factors, including scalability and maintenance. These elements impact your resources, site speed, and user experience. Understand the differences to grow and maintain your business’s online presence effectively.
Growing With Your Business Needs
As your business evolves, so do your digital tracking needs. A system that scales with you is vital. Both GTM server-side and client-side have unique scalability features:
- Server-side GTM allows offloading tasks from the client. This can reduce the strain on your website, leading to faster load times as traffic increases.
- Client-side GTM is easier to set up and can be sufficient for smaller websites. However, it might encounter performance bottlenecks as you grow.
Assess your long-term goals and current technical infrastructure when deciding. A balanced approach might involve starting client-side and transitioning to server side as demand grows.
Ease Of Tag Management Maintenance
Maintenance is critical to keep your site’s data collection accurate and efficient. Here’s how both options stack up:
| Aspect | Server-side GTM | Client-side GTM |
|---|---|---|
| Updates | Easier to manage centrally | Requires manual updates on the site |
| Security | Greater control over data | Dependent on browser policies |
| Compatibility | Future-proof for new tech | May need frequent adjustments |
Consider the human and technical resources you have for maintenance. A well-maintained GTM environment ensures peak performance and reliable data for your decision-making processes.
Integrating With Third-party Services
Integrating with third-party services is a crucial choice for businesses looking to expand their capabilities in data analytics and marketing. It can profoundly impact the performance, accuracy, and security of data collection. Understanding the nuances between server-side and client-side integrations is essential for a successful strategy.
Compatibility With Analytics And Marketing Tools
Different tools often require specific integration methods to function optimally. Compatibility is king when choosing how to integrate your analytics and marketing tools.
- Google Analytics: Offers both client-side and server-side tracking options.
- Facebook Pixel: Works with both methods but may need additional configuration for server-side.
- Email Marketing Platforms: Typically incorporate client-side integration for ease of use.
A thorough compatibility check ensures seamless integration with your preferred services.
Server-side Versus Client-side Integrations
| Comparison Aspect | Server-Side Integration | Client-Side Integration |
|---|---|---|
| Data Security | Higher, due to controlled server environment | Lower, as data is exposed to client-side risks |
| Performance | Can reduce page load times by offloading tasks | Potentially slower, affects user experience |
| Flexibility | Customizable, server logic can be changed easily | Easy to implement with existing website structures |
Selecting the right integration method depends on balancing the need for data security, performance, and adaptability. Server-side offers controlled data processing, while client-side shines in ease of implementation.
Cost And Resource Investment
When comparing GTM Server-Side and Client-Side, cost and resource investment matter. These factors influence the decision-making process. Understanding the financial and technical commitments is vital. Let’s delve into an analysis of the investment implications of each approach.
Analyzing The Cost-benefit
GTM Server-Side and Client-Side tracking both come with distinct expenses. Server-Side may save on third-party requests, reducing costs. Client-side often involves lower upfront fees. Here’s a breakdown:
- GTM Server-Side:
- Reduces third-party requests
- May cut down on external service costs
- Offers robust data processing options
- Client-Side:
- Has minimal initial setup costs
- Less complex server requirements
- Can be more affordable short-term
Choosing the right model needs a balance between current costs and future savings.
Required Investment In Infrastructure
Infrastructure investment varies greatly between GTM Server-Side and Client-Side. Below is an easy-to-understand outline:
| Aspect | GTM Server-Side | Client-Side |
|---|---|---|
| Servers | Stronger servers needed | Basic hosting suffices |
| Technical Skill | Higher expertise required | Manageable with basic knowledge |
| Maintenance | Ongoing investment | Less frequent updates |
Server-Side demands more robust servers and technical skills. It requires ongoing maintenance costs. Client-side setup is simpler and often less expensive. Each choice calls for careful consideration of your team’s capabilities and the available budget.

Credit: medium.com
Making The Decision: Server-side Or Client-side
Making the right choice between server-side and client-side tagging can be a game-changer for a business. It affects how data gets handled, website performance, and user privacy. Each approach has unique advantages and considerations.
Tailoring To Business Requirements
Identifying the specific needs of a business is crucial. Server-side tagging offers robust data control and security, making it ideal for businesses handling sensitive customer information. This method reduces the amount of JavaScript executed on the user’s device, potentially improving page load times and user experience.
In contrast, client-side tagging is easier to implement and debug. It allows for real-time data collection. Here are key factors to consider:
- Data Sensitivity: Server-side is preferred for sensitive data.
- Technical Resources: The client side requires fewer technical resources.
- Performance Goals: Server-side may boost website performance.
Best Practices For Implementation
To ensure a successful implementation, follow these best practices:
- Start with clear objectives for data collection and analysis.
- Document the tagging process thoroughly.
- Test extensively before full deployment.
For server-side, emphasize security protocols and validate data servers. For the client side, focus on the end-user experience and page load speeds.
Future-proofing Your Tagging Strategy
With new privacy regulations and web technologies evolving, a future-proof tagging strategy is vital. Consider adopting a hybrid approach. Combine server-side and client-side for flexibility and control. Keep an eye on industry trends and adjust your strategy accordingly to stay ahead.
Auditing and updating tags regularly ensures that your tagging strategy remains effective and compliant with the latest standards.

Credit: infotrust.com
Frequently Asked Questions On Gtm Server-side Vs Client-side
What Is The Difference Between Client-side Gtm And Server-side Gtm?
Client-side GTM tracks user interactions directly within the browser. Server-side GTM processes data on a server, offering more control and improved data privacy.
What Is the Difference Between Server-side And Client-side?
Server-side refers to operations performed on the server, affecting website functionality. Client-side means processes running on the user’s browser, often affecting interface and experience.
What Is The Difference Between Client-side Tracking And Server-side Tracking?
Client-side tracking collects user data via the browser, typically with cookies or JavaScript. Server-side tracking processes data on the server, offering better data security and privacy.
Is Server-side Tracking The Same As Tagging?
Server-side tracking and tagging are not identical. Server-side tracking processes data on a server, while tagging involves adding code snippets to a webpage to track user interactions.
What Is Gtm Server-side Tagging?
Server-side tagging in Google Tag Manager (GTM) lets you handle and process data on a server, providing better user privacy and faster page loads.
Conclusion
Navigating the complexities of GTM server-side and client-side tracking requires careful consideration. Both methods have distinct benefits, tailored to specific business needs and privacy concerns. As you strategize your analytics approach, weigh these options to enhance data accuracy and website performance.
Remember, the choice is not universal; it’s about finding the right balance for your site’s unique ecosystem.